Ubuntu 11.10 (Oneiric Ocelot) is one of the most popular operating system for programming because there are lot of great open source applications, tools, compilers, debuggers, IDEs are available free of cost. Some of them are – GCC – The greatest compiler for C language (from FSF (‘Free Software Foundation’ by Stallman); Linux Torwalds used GCC while developing Linux Kernel), Eclipse IDE (The most popular ‘Integrated Development Environment’ for Java programmers), Netbeans, KDevelop, Codelite etc.
C/C++ language is a high level programming language (although the term high and low is used in relative sense e.g C is a high level language as compared to Assembly but if we compare it with java then C is a low level programming language; the term high or low basically describes the closeness with hardware). Most of the operating systems has been written in C language. This post has been written for beginners who just started learning C/C++ or the programmers who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu (although the commands are almost same for all Linux based operating system).
Compiling and Executing C program in Ubuntu 11.10
1. Write and save the program
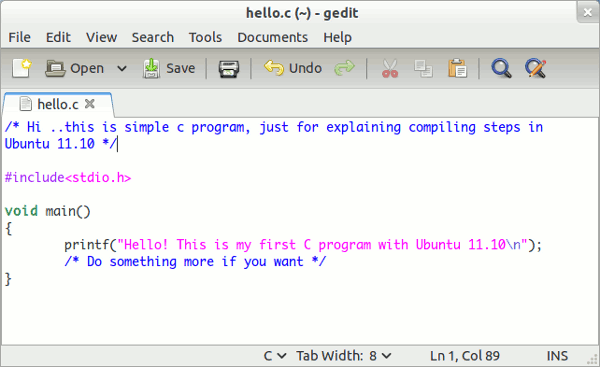
Open a simple text editor (e.g gedit), IDE (Eclipse) or command line code editor (Nano or Vim). I’ll be using gedit as it is very simple to use and it’s recommended for beginner programmers. Right Click on Desktop or any directory (Browse File using Nautilus) and select create new File – hello.c (.c extension is used to indicate that it’s a c program). Then write a simple program like this (and save the program press Ctrl+S)
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf("Hello! This is my first C program with Ubuntu 11.10\n");
/* Do something more if you want */
}
2. Compile the program
GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) is installed by default, in Ubuntu. To compile the program, open the terminal and move on to the target directory type the command – (where gcc implies compiler name, then it asks for the file name of the source program while -o option specifies the file name of the output program)
gcc hello.c -o hello1
If there is no syntax/semantic error in you program then the compiler will successfully generate an executable file, otherwise fix the problem in your code.
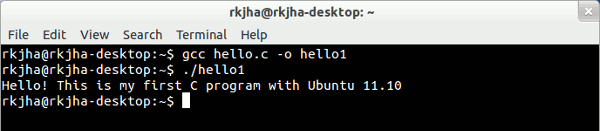
3. Execute the program
To execute the program, you need to run –
./hello1
Compiling and Executing C++ program
The steps are almost same as above but you need to install g++ compiler, the file extension should be .cpp and in compilation phase replace gcc with g++. To install G++ compiler, execute the command –
sudo apt-get install g++
If you have any problems then share it through comments. One more thing, This video might help you in running your first C program in Ubuntu 11.10(I’ve recorded it in Gnome Shell interface) –

i will like to know “how to run java program on ubuntu 11.10”
goto that directory then
javac prog.java
java classname
Is there any way to delete the ugly Unity Dock? Because I use Cairo Dock, which is far better than Unity Dock.
The error tells me ‘::main’ must return ‘int’…
In C++ main is int not void and returns 0 if successful.
Change void main() to be int main()
you can compile and run c code simply
compile: cc hello.c
run: ./a.out
I found this message while installing g++
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock – open (11: Resource temporarily unavailable)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), is another process using it?
What is the problem?
It’s because you’r still downloading another software from maybe software manager or terminal at that very moment 😀
Can you help me to solve a problem?
I am trying to compile separate header files as follows:
“declarations.h”
#ifndef DECLARATIONS_H
#define DECLARATIONS_H
{
//declarations
}
#endif
“definitions.cpp”
#include “declarations.h”
{
//definitions
}
“main.cpp”
#include “declarations.h”
int main()
{
//some code
}
When I attempt to compile, an error is returned as follows:
“undefined reference to function xyz” (included in file “definitions.cpp”)
I know that the code works because if I put the definitions in “declarations.h” then it all works fine.
I am using Ubuntu 11.10 and compiling at the command line using the gcc compiler using simply c++ -o main main.cpp
The answer is to compile using:
c++ -o targetfilename main.cpp definitions.cpp
Separate compilation is also possible using:
c++ -c definitions.cpp
c++ -c main.cpp
c++ -o targetfilename definitions.o main.o
Thanks to gcc documentation for this.
hey pls tell me is it possible to write microprocessor prgms??? means masm.. if so means tell me the steps
add.cpp:1:21: fatal error: iostream.h: No such file or directory
compilation terminated.
guys pls tell me how to ovr com from this.. i’m unable to execute c++.. give me the solution plssss
write iostream instead of iostream.h and it’ll compile if you dont have any other error.
I feel happy to see the program. waiting to see more mathematical program
Nice little demo, thank you.
well this works when I keep the c or c++ file in Ubuntu’s home directory. But I tried the same thing, the only difference was that I was keeping the file in windows drive and accessing it through terminal. The compilation was fine but when I tried to execute the program it gave an error message that “PERMISSION DENIED” how to overcome this problem ?
From where i can get the G++ dbi package??
help me with this…
after typin the command sudo apt-get install g++,i got the error as failed to fetch the archive in linux mint.
thank u… i make my program run
thx really it was very helpful for me..:)
highly helpful post.thnks
This is a very helpful article about C++. Those who are having difficulties in compiling and running such in Ubuntu OS will surely find this post informative. Thanks for sharing.
while installing g++ it said command not found please help me…
thanks a lot,it was so helpful to me
how to execute puts() and gets() statements?
wat is d compilation step n any syntax should be included?
I compile the program like g++ HELLO.CPP -o hello1
How I resole in ubuntu 16.04 :
fatal error: conio: No such file or directory